Exploring the Spectrum of Human Variation: Understanding Gender Differences
Related Articles: Exploring the Spectrum of Human Variation: Understanding Gender Differences
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Spectrum of Human Variation: Understanding Gender Differences. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the Spectrum of Human Variation: Understanding Gender Differences
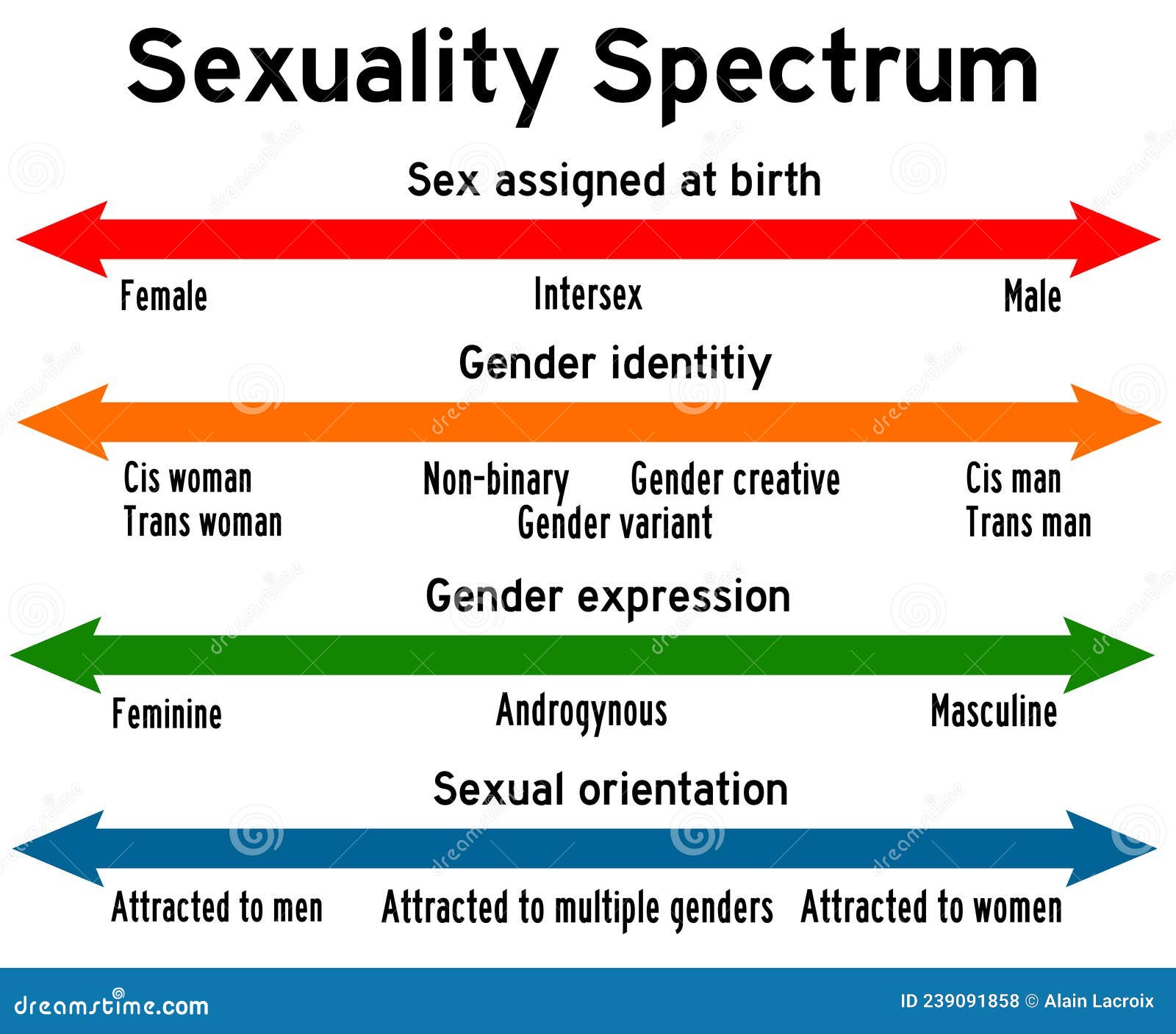
The human experience is a tapestry woven with threads of countless individualities, and gender is one of the most prominent and complex threads. While the concepts of "male" and "female" are often presented as binary opposites, the reality is far more nuanced. Understanding the differences between men and women requires a multifaceted approach that acknowledges the vast spectrum of human variation and recognizes the influence of biological, social, and cultural factors.
Biological Differences:
While the biological differences between men and women are undeniable, they are not absolute. There is a significant degree of overlap in biological characteristics, and individuals within each gender category exhibit a wide range of variations.
- Chromosomes: Men typically possess an X and a Y chromosome, while women typically have two X chromosomes. This fundamental difference influences the development of primary and secondary sexual characteristics.
- Hormones: Men produce higher levels of testosterone, a hormone associated with muscle mass, aggression, and libido. Women, on the other hand, produce higher levels of estrogen and progesterone, hormones linked to reproductive functions and emotional regulation.
- Physical Attributes: Men generally have larger muscle mass, taller stature, and a higher bone density. Women, on average, have a higher percentage of body fat and a lower center of gravity.
- Reproductive Systems: Men and women have distinct reproductive systems, with men possessing a penis and testes, and women having a vagina, uterus, and ovaries. These differences are essential for sexual reproduction.
Cognitive and Behavioral Differences:
The differences in cognitive abilities and behaviors between men and women are often debated, with research findings often conflicting. It is crucial to recognize the impact of social and cultural influences on these observed differences.
- Spatial Reasoning: Some studies suggest that men may have a slight advantage in spatial reasoning tasks, such as mental rotation and map reading. However, these differences are often small and can be influenced by experience and training.
- Verbal Abilities: Women are often perceived as having stronger verbal abilities, particularly in areas like fluency and vocabulary. However, this perception is not universally supported by research, and factors like socioeconomic status and education level play a significant role.
- Emotional Expression: Women are often stereotyped as being more emotionally expressive than men. While this stereotype may hold some truth, it is important to acknowledge the influence of social expectations and cultural norms on emotional expression.
- Communication Styles: Men and women often exhibit different communication styles, with men tending to be more direct and task-oriented, while women may be more indirect and relationship-focused. However, these are generalizations, and individual communication styles vary widely.
Social and Cultural Influences:
Gender roles and expectations are deeply ingrained in societies around the world. These societal constructs shape the way men and women are perceived, treated, and how they behave.
- Gender Stereotypes: Stereotypes about men and women can influence their self-perception, limit their opportunities, and create barriers to equality. These stereotypes are often based on outdated assumptions and can be harmful.
- Gender Roles: Traditional gender roles often assign specific responsibilities and expectations to men and women. These roles can limit individual choices and opportunities, hindering personal growth and societal progress.
- Cultural Variations: Gender roles and expectations vary significantly across cultures. What is considered masculine or feminine in one culture may be different in another, highlighting the dynamic and fluid nature of gender norms.
Importance of Understanding Gender Differences:
Understanding gender differences is crucial for fostering a more equitable and inclusive society. By acknowledging the biological, cognitive, and social factors that contribute to these differences, we can:
- Challenge Gender Stereotypes: Recognizing the limitations of stereotypes and promoting a more nuanced understanding of gender can help break down harmful assumptions and create a more equitable environment.
- Promote Gender Equality: Understanding the challenges faced by different genders allows us to advocate for policies and practices that address systemic inequalities and create a level playing field.
- Enhance Communication and Relationships: Recognizing and respecting different communication styles and perspectives can lead to more effective communication and stronger relationships.
- Improve Education and Healthcare: Understanding gender-specific needs can lead to more tailored educational programs and healthcare services that address the unique challenges faced by different genders.
FAQs:
-
Are men and women inherently different?
- While there are biological differences between men and women, these differences are not absolute and do not dictate individual abilities or behaviors.
-
Can men and women be equal if they are different?
- Yes, equality does not mean sameness. It means recognizing and respecting differences while ensuring that individuals have equal opportunities and rights regardless of gender.
-
Why are there so many gender stereotypes?
- Gender stereotypes are often rooted in historical and cultural factors that have shaped societal expectations and norms. These stereotypes can be perpetuated through media, education, and family dynamics.
-
What can I do to challenge gender stereotypes?
- Be mindful of your own language and actions. Challenge stereotypes when you encounter them. Support organizations and initiatives that promote gender equality.
-
How can we create a more inclusive society for everyone?
- By embracing diversity and challenging discrimination, we can create a society where everyone feels valued, respected, and empowered.
Tips:
- Be mindful of your own biases: Everyone holds unconscious biases, and it is important to be aware of them and actively challenge them.
- Listen attentively to diverse perspectives: Seek out information and experiences from individuals of different genders to gain a deeper understanding of their perspectives.
- Promote inclusive language: Use language that is gender-neutral and avoids reinforcing stereotypes.
- Support organizations that advocate for gender equality: Donate your time, resources, or expertise to organizations working to advance gender equality.
- Educate yourself and others: Share information about gender differences and the importance of challenging stereotypes.
Conclusion:
The differences between men and women are complex and multifaceted. While biological differences are undeniable, it is crucial to recognize the significant role of social and cultural factors in shaping gender roles and expectations. By understanding these differences and challenging harmful stereotypes, we can foster a more equitable and inclusive society where individuals are empowered to reach their full potential regardless of gender. Ultimately, embracing the spectrum of human variation and recognizing the inherent worth of every individual is essential for building a just and compassionate world.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Spectrum of Human Variation: Understanding Gender Differences. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!