Exploring the Spectrum of Human Diversity: Understanding Sex and Gender Differences
Related Articles: Exploring the Spectrum of Human Diversity: Understanding Sex and Gender Differences
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Spectrum of Human Diversity: Understanding Sex and Gender Differences. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the Spectrum of Human Diversity: Understanding Sex and Gender Differences
The human experience is a tapestry woven with threads of countless variations, and among these variations, sex and gender differences stand out as prominent threads. While the concept of "men vs. women" often evokes a binary framework, the reality is far more complex and nuanced. This exploration delves into the intricate interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors that contribute to the diverse spectrum of human differences, highlighting the importance of understanding these differences for fostering inclusivity and promoting a more equitable society.
Biological Differences: A Foundation for Understanding
Sex, a biological construct, refers to the distinct physical characteristics that differentiate males and females. These differences are primarily rooted in genetics, with the presence of XX chromosomes defining female biological sex and XY chromosomes defining male biological sex. This fundamental difference in genetic makeup leads to a cascade of physiological distinctions, including:
- Hormonal Profiles: Males typically produce higher levels of testosterone, contributing to greater muscle mass, bone density, and a deeper voice. Females, on the other hand, produce higher levels of estrogen and progesterone, which influence reproductive development and cyclical hormonal fluctuations.
- Reproductive Systems: The biological differences are most evident in the reproductive systems, with males possessing external genitalia, testes, and a prostate, while females have internal genitalia, ovaries, and a uterus.
- Physical Attributes: Men tend to be taller and heavier than women, with a higher proportion of muscle mass. Women generally have a higher percentage of body fat, contributing to a different body shape and distribution of fat.
Beyond Biology: Exploring Gender and its Influence
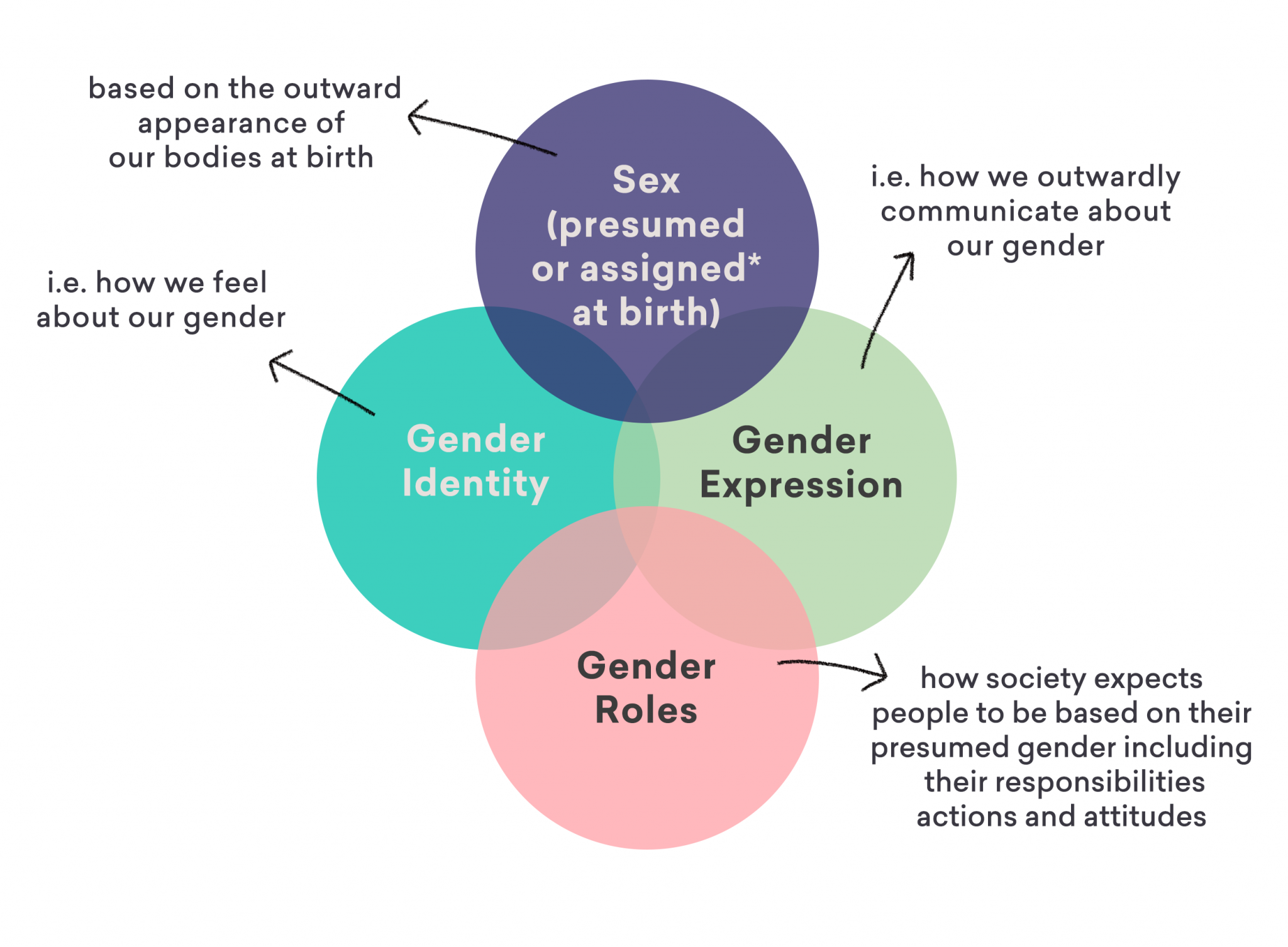
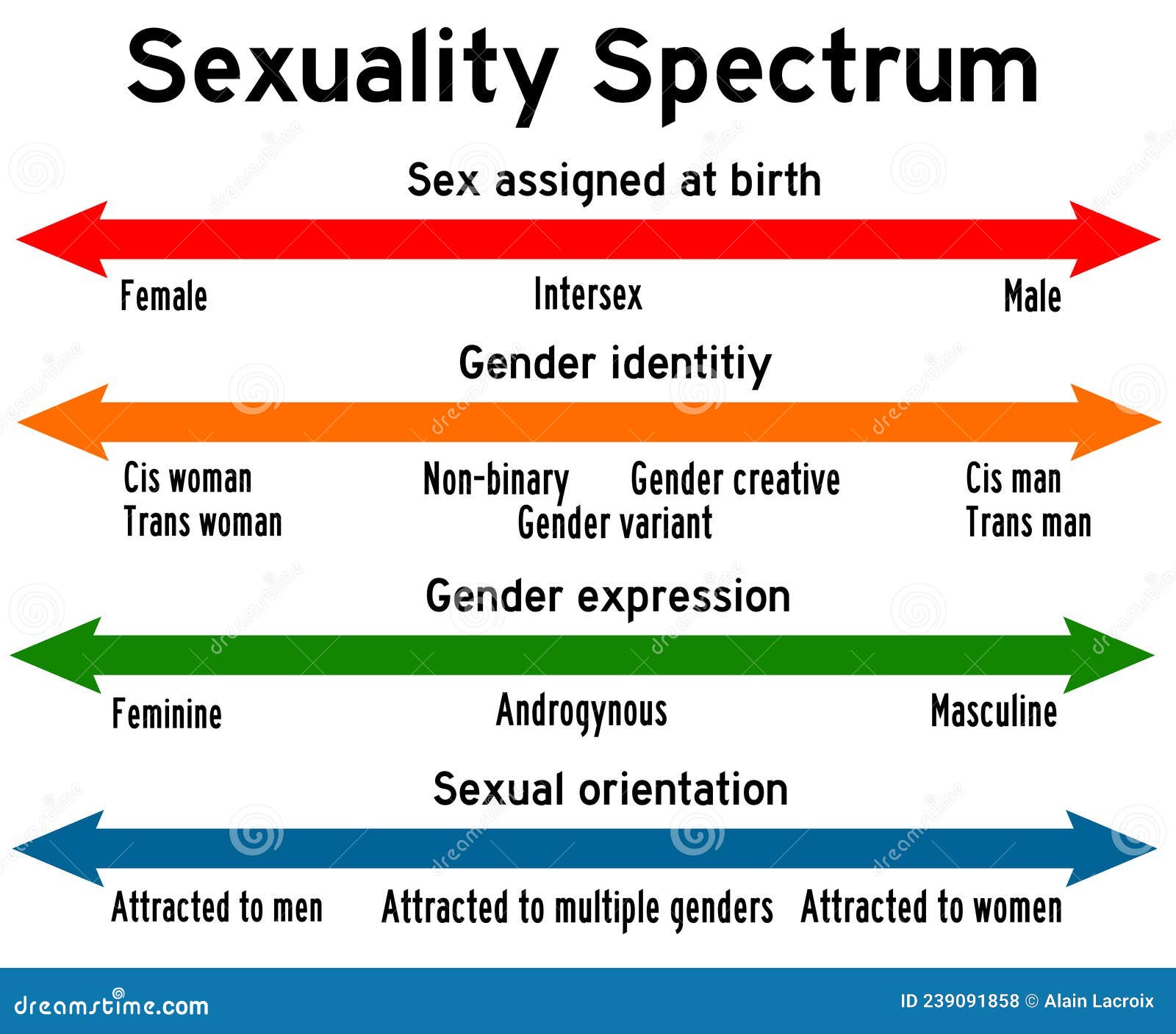
While biological sex provides a foundational framework, gender is a social construct that encompasses the roles, behaviors, expressions, and identities that a society associates with being male or female. Gender is fluid and dynamic, influenced by cultural norms, personal experiences, and individual choices. It is important to acknowledge that gender identity and expression can differ from biological sex, and individuals may identify as male, female, non-binary, or transgender.
Cognitive Differences: Exploring the Spectrum
The question of cognitive differences between men and women has sparked considerable debate. While some studies suggest potential differences in areas like spatial reasoning, verbal fluency, and emotional processing, these differences are often subtle, with significant overlap between the sexes. It is crucial to avoid generalizations and recognize the vast individual variation within each sex.
- Spatial Reasoning: Some studies indicate that men may have a slight advantage in tasks requiring spatial reasoning, such as mental rotation and navigation. However, these differences are not universal, and many women excel in these areas.
- Verbal Fluency: Women tend to outperform men in tasks requiring verbal fluency, such as language comprehension and vocabulary. However, this difference is not absolute, and many men exhibit strong verbal abilities.
- Emotional Processing: Research suggests that women may be more attuned to emotional cues and may express emotions more readily. However, these differences are complex and influenced by cultural norms and social expectations.
Social and Cultural Influences: Shaping Gender Roles
Gender roles, the expectations and behaviors associated with each gender, are deeply embedded within societal structures and cultural norms. These roles can significantly influence individual choices, opportunities, and experiences.
- Traditional Gender Roles: Historically, societies have often prescribed distinct roles for men and women, with men expected to be the breadwinners and women responsible for domestic duties. These traditional roles have evolved over time, but their remnants continue to influence gender expectations.
- Gender Stereotypes: Stereotypes, often based on generalizations and biases, perpetuate assumptions about men and women’s abilities, interests, and behaviors. These stereotypes can limit opportunities and create barriers for individuals who do not conform to societal expectations.
Understanding the Importance of Differences
Acknowledging and understanding sex and gender differences is not about perpetuating stereotypes or reinforcing inequalities. Instead, it is about recognizing the unique strengths and perspectives that each individual brings to the table. This understanding is crucial for:
- Promoting Inclusivity: By recognizing and valuing the diversity of human experiences, we can create more inclusive environments that respect and accommodate individual differences.
- Fostering Equity: Understanding the social and cultural factors that shape gender roles allows us to challenge inequalities and advocate for equal opportunities for all.
- Enhancing Communication: Recognizing the potential for different communication styles and perspectives can improve communication and collaboration.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Are there any significant differences in brain structure between men and women?
A: While some studies have shown subtle differences in brain structure and function, these differences are not universal and do not necessarily translate into significant cognitive disparities. The vast majority of the brain is identical between sexes, and individual variation within each sex is far greater than any average differences.
Q: Do men and women have different communication styles?
A: Research suggests that men and women may communicate differently, with men tending to be more direct and task-oriented, while women may be more indirect and relationship-focused. However, these are broad generalizations, and individual communication styles vary greatly.
Q: Do men and women experience emotions differently?
A: While some studies suggest that women may be more attuned to emotions and express them more readily, these differences are complex and influenced by cultural norms and social expectations. Men and women are capable of experiencing a wide range of emotions, and individual differences in emotional expression are significant.
Tips for Understanding and Respecting Differences
- Challenge Stereotypes: Be mindful of gender stereotypes and actively challenge them when you encounter them.
- Listen with Empathy: Approach conversations with an open mind and a willingness to understand different perspectives.
- Respect Individuality: Recognize that individuals within each gender group are diverse and unique.
- Advocate for Equity: Support policies and initiatives that promote equal opportunities for all.
Conclusion
The human experience is a tapestry woven with countless threads of variation, and sex and gender differences are among the most prominent. While biological differences provide a foundation for understanding, gender is a social construct shaped by cultural norms, personal experiences, and individual choices. Recognizing and understanding these differences is not about perpetuating stereotypes but rather about appreciating the unique strengths and perspectives that each individual brings to the table. By embracing diversity, fostering inclusivity, and promoting equity, we can create a society that celebrates the full spectrum of human experience.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Spectrum of Human Diversity: Understanding Sex and Gender Differences. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!